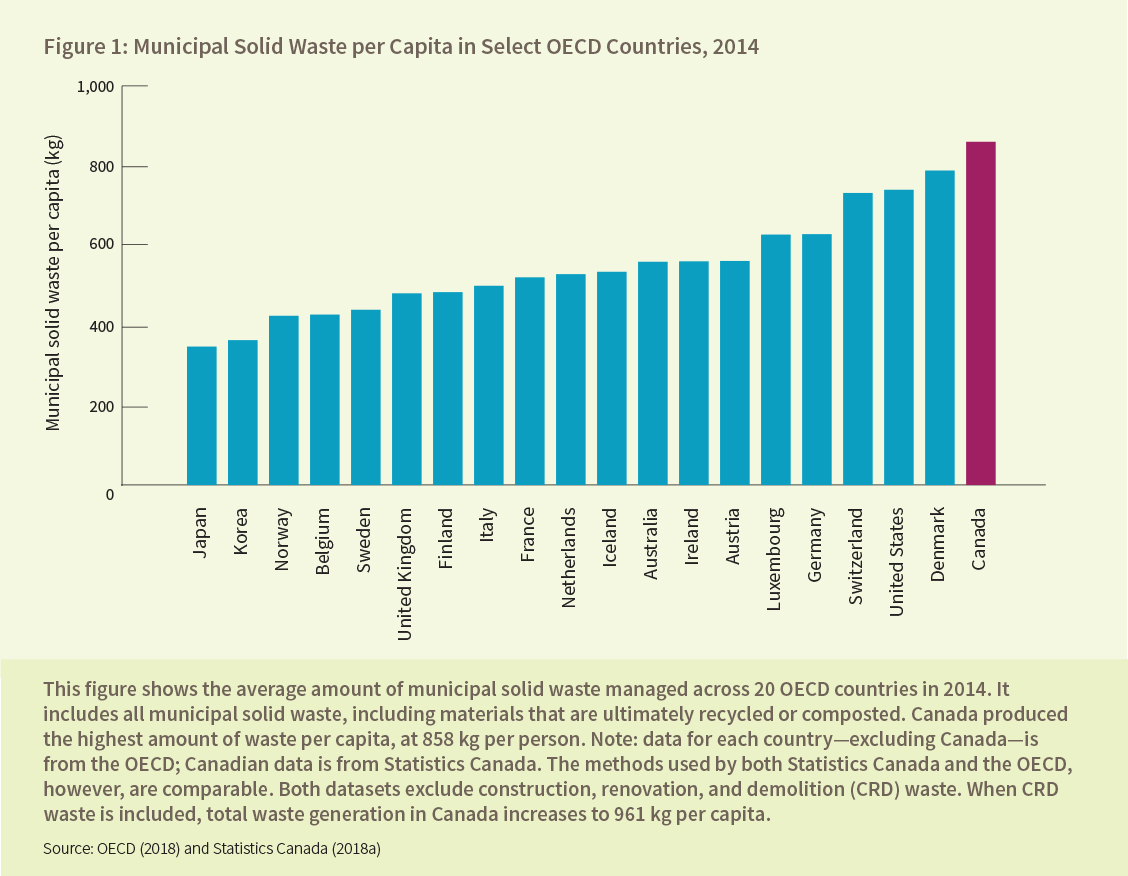
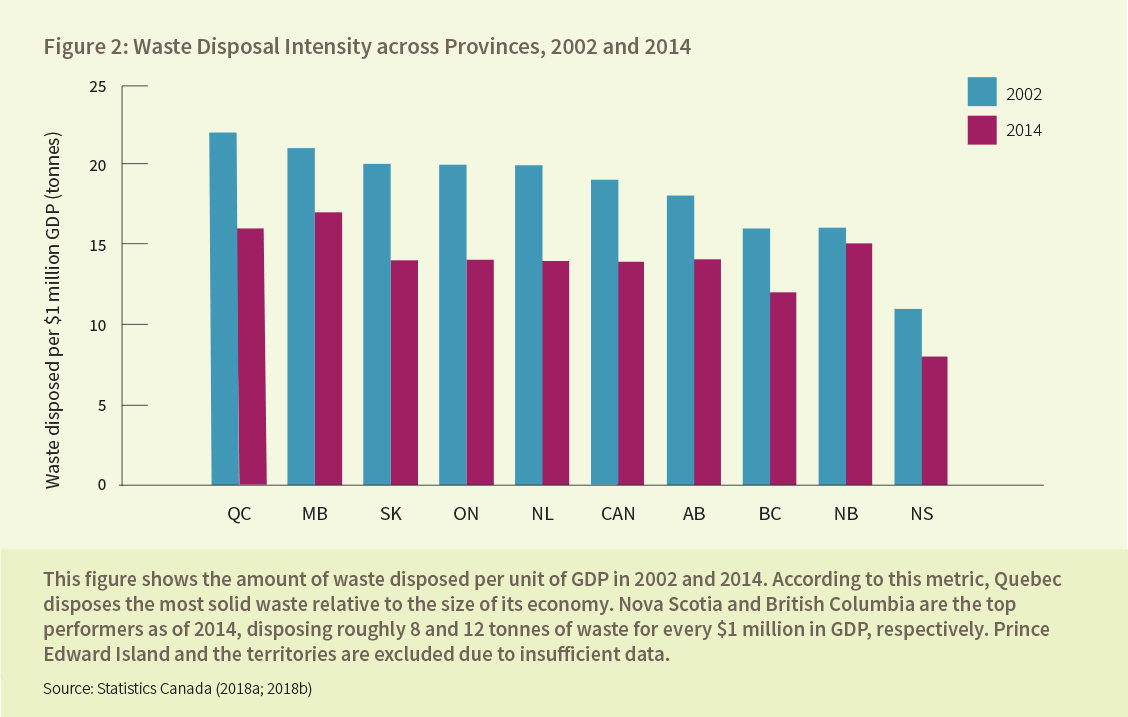
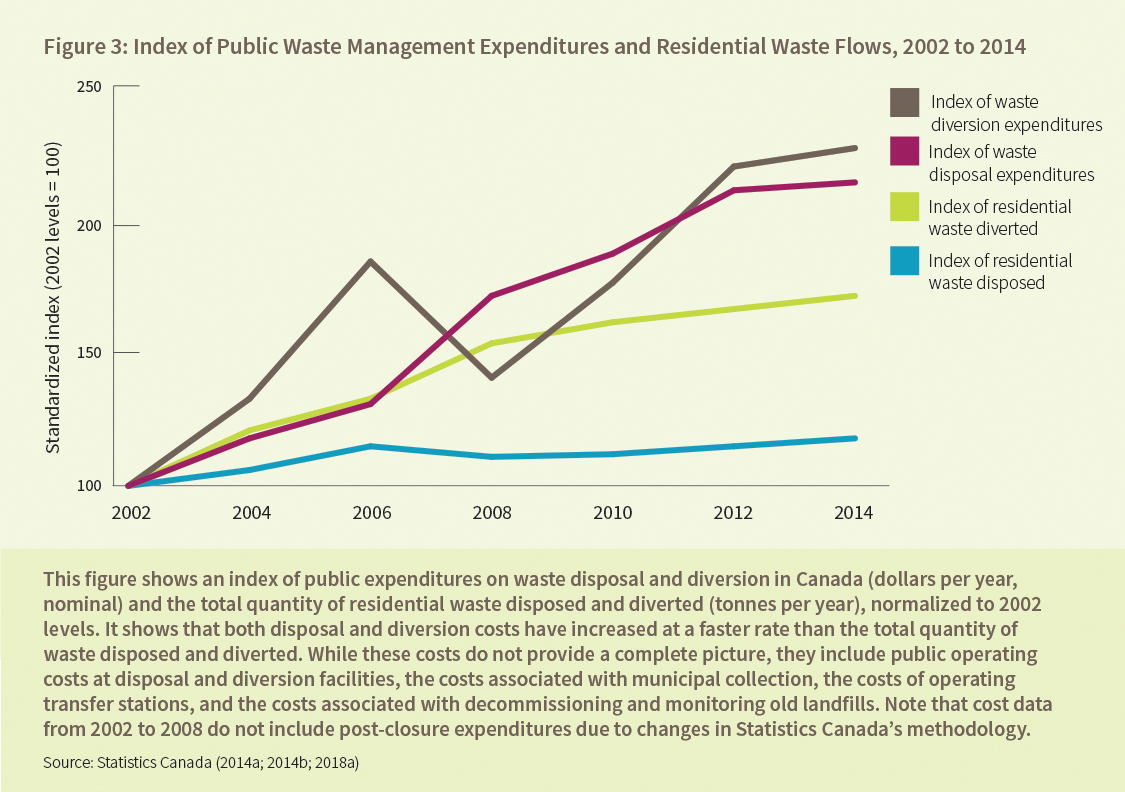
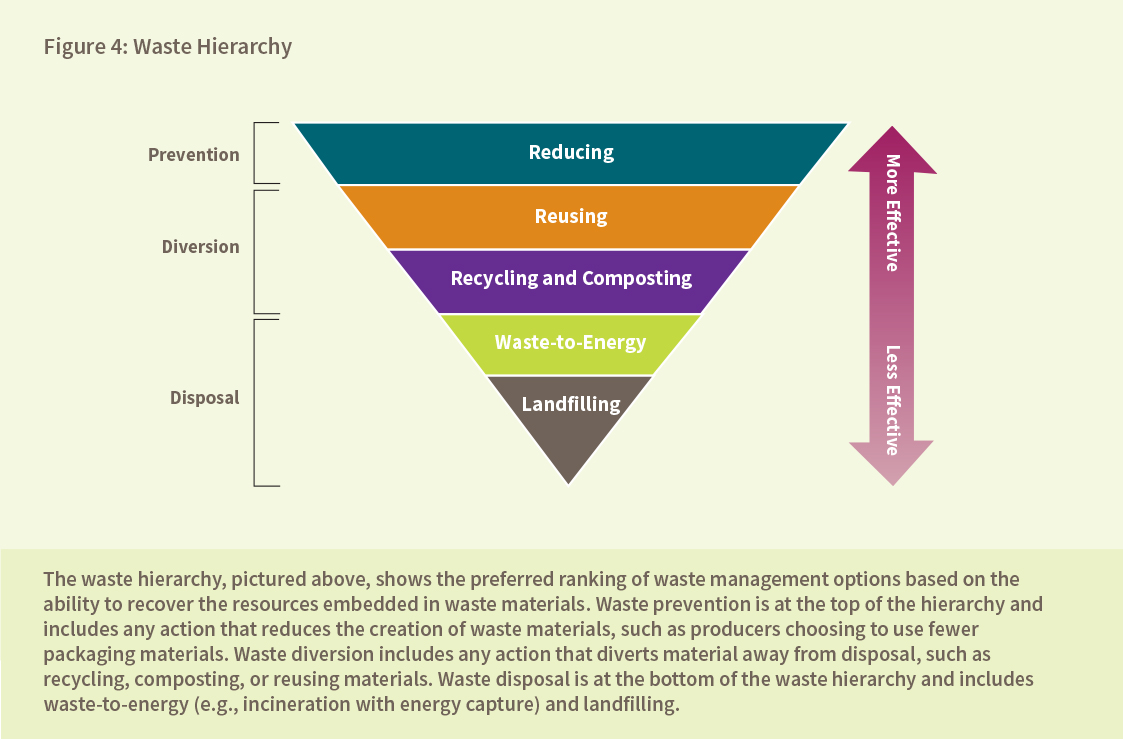
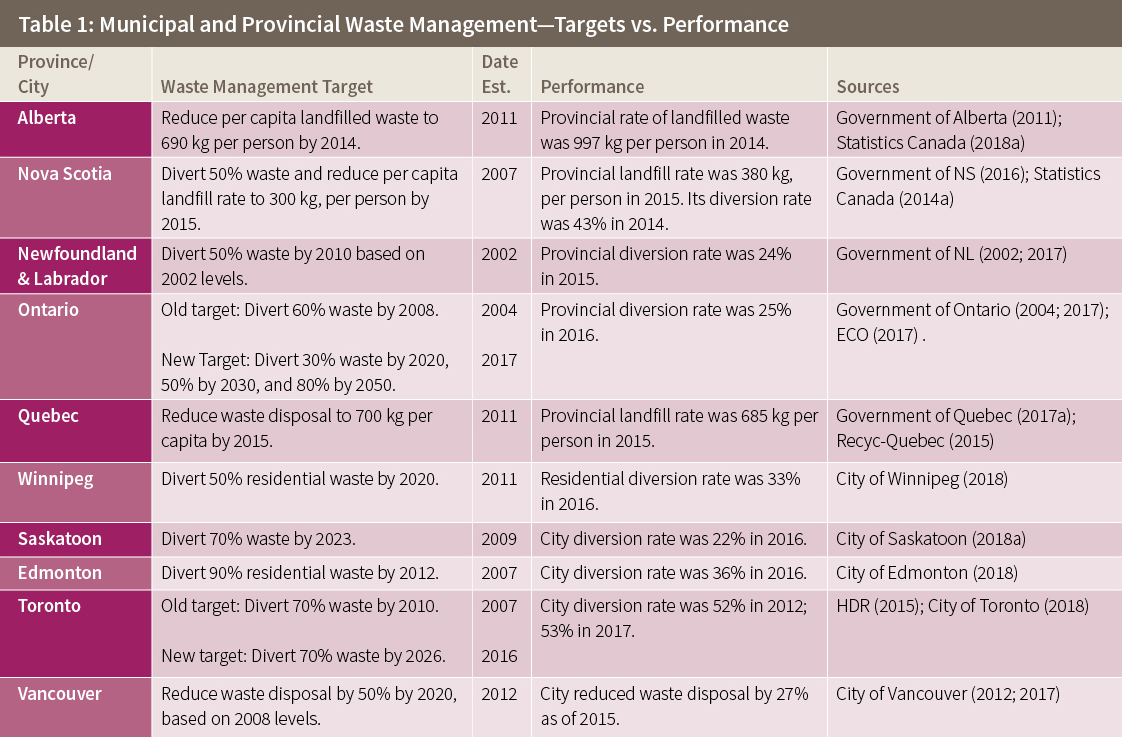
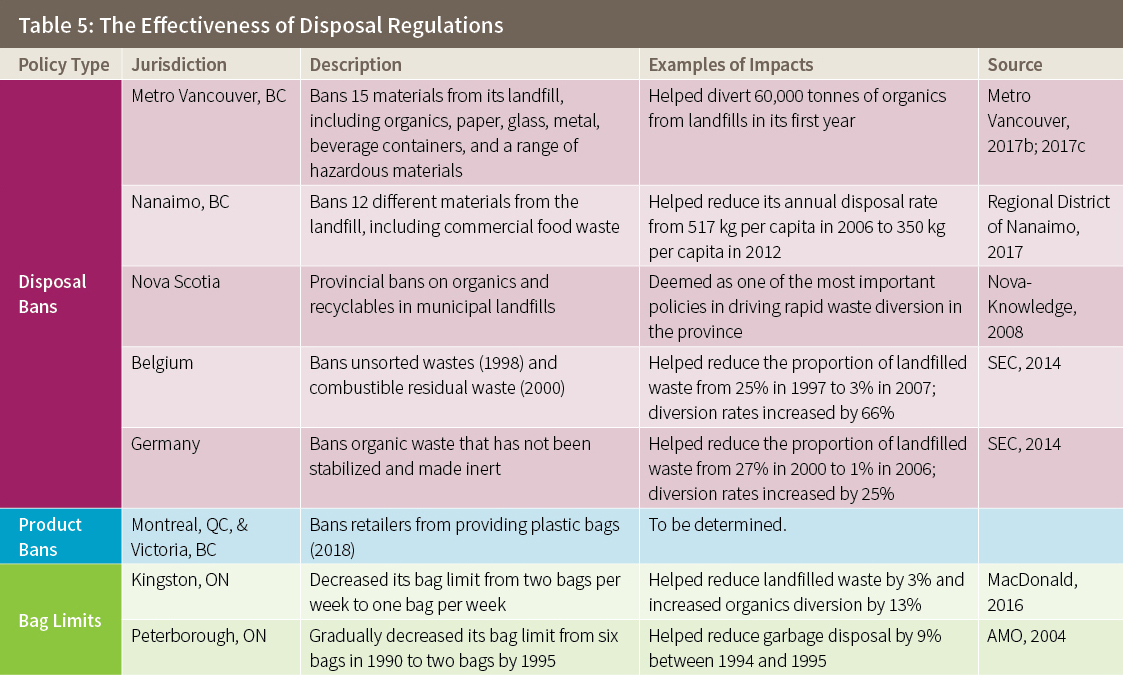
An Open Letter from Economists on Canadian Carbon Pricing
2024-03-28
As economists from across Canada, we are concerned about the significant threats from climate change. We encourage governments to use economically sensible policies to reduce emissions at a low cost, address Canadians’ affordability concerns, maintain business competitiveness, and support Canada’s transition to a low-carbon economy. Canada’s carbon-pricing policies do all those things.
There is plenty of discussion about carbon pricing in Canada today. Healthy public debate is good, but it should be based on sound evidence and facts. Let’s examine some of the claims made by critics of carbon pricing and compare them with what the evidence shows.